Digital marketing delivers measurable ROI that traditional marketing methods struggle to match. SEO campaigns alone can achieve returns of up to 1,031% in specific industries. But comparing the effectiveness of digital and traditional marketing requires a systematic approach focused on specific, measurable metrics. This analysis breaks down six key performance indicators that provide a clear framework for evaluating marketing ROI across both channels.
Marketing success depends on accurate measurement and strategic implementation of both digital and traditional channels. By examining these metrics in detail, you’ll gain the insights needed to optimize your marketing budget allocation and maximize returns across all channels.
This analysis combines comprehensive digital marketing analytics with traditional marketing metrics to provide a complete picture of marketing effectiveness.
Each section includes practical implementation guidance and strategic recommendations for optimizing your marketing investments.
Understanding Marketing ROI Measurement
Marketing ROI measurement has transformed dramatically with the rise of digital channels. The global digital marketing market is projected to reach $786.2 billion by 2026, driven by superior measurement capabilities and precise tracking methods. This growth reflects the increasing demand for accountable, measurable marketing investments.
The Evolution of Marketing Metrics
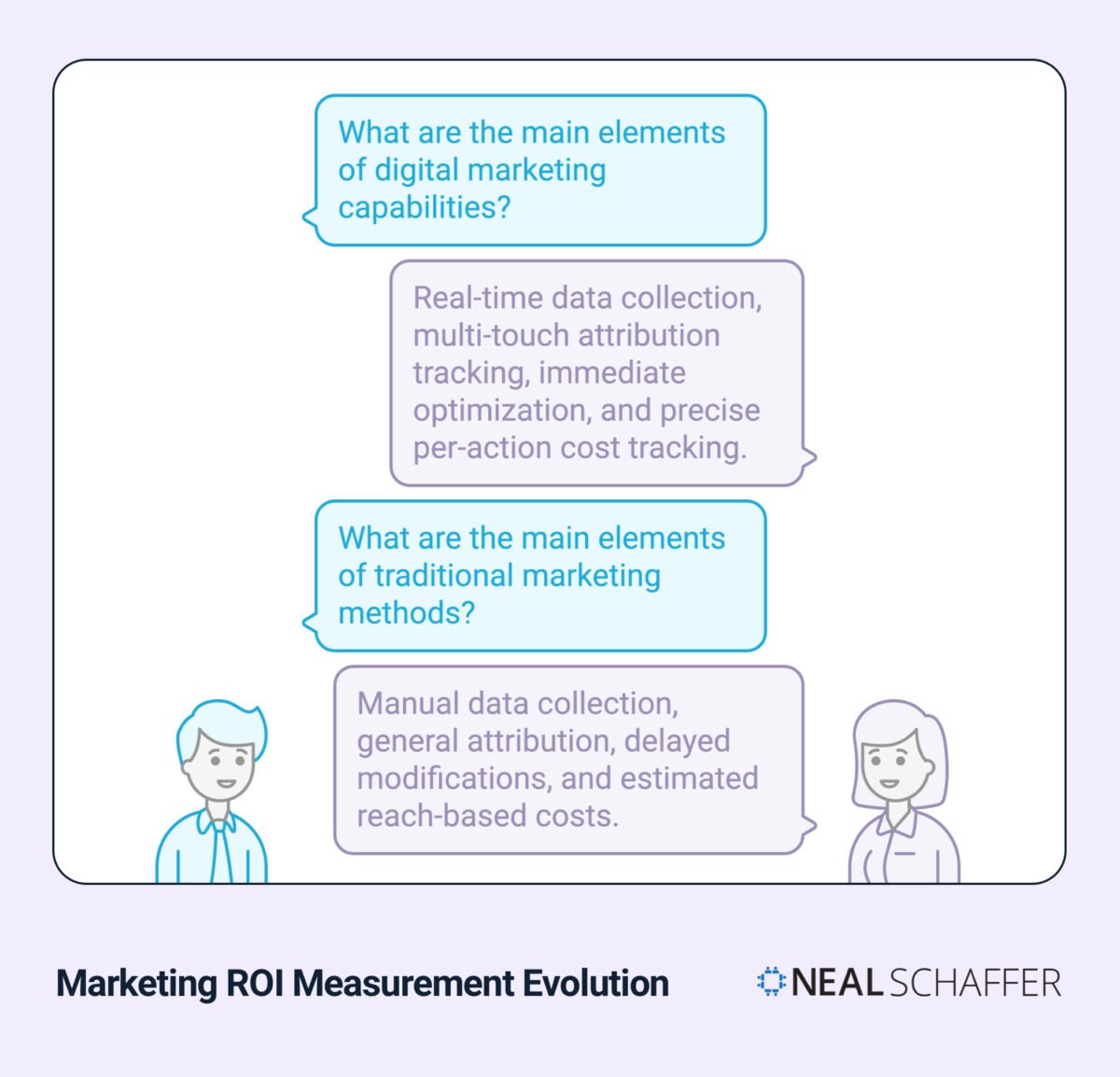
Digital marketing provides granular tracking capabilities through tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Ads Manager, and other digital marketing tools. These platforms enable real-time monitoring of key performance indicators, allowing for immediate campaign adjustments and optimization. Traditional marketing, while still valuable, relies on broader measurement methods such as surveys, focus groups, and estimated reach calculations.
| Measurement Aspect | Digital Marketing | Traditional Marketing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Real-time, automated | Manual, periodic |
| Attribution | Multi-touch tracking | General attribution |
| Adjustment Speed | Immediate optimization | Delayed modifications |
| Cost Tracking | Precise per-action | Estimated reach-based |
Current Challenges in ROI Tracking
The primary challenge in comparing traditional and digital marketing ROI lies in establishing equivalent measurement frameworks. Digital channels provide detailed marketing KPIs and conversion data, while traditional methods often require indirect measurement techniques. This disparity necessitates a strategic approach to performance evaluation.
Key considerations for comprehensive ROI tracking include:
- Integration of online and offline data sources
- Standardization of measurement metrics across channels
- Implementation of cross-channel attribution models
- Consideration of both short-term and long-term impact
Understanding these fundamental differences in measurement capabilities provides the foundation for effective marketing resource allocation. The next section examines specific metrics for calculating Cost per Lead (CPL) and Cost per Acquisition (CPA) across both traditional and digital channels, offering practical frameworks for ROI comparison.
1. Cost per Lead (CPL) and Cost per Acquisition (CPA) Analysis
Cost per Lead and Cost per Acquisition serve as fundamental metrics for comparing marketing channel effectiveness. Digital marketing channels demonstrate superior efficiency, with email marketing generating $42 for every $1 spent. This remarkable return highlights the cost-effectiveness of digital channels when properly implemented and tracked.


Digital Marketing CPL Metrics
Digital marketing enables precise tracking of lead generation costs through advanced analytics platforms. The calculation framework provides clear insights into campaign effectiveness:
Digital CPL Formula:
Total Campaign Spend ÷ Number of Leads Generated = Cost per Lead
Example: $5,000 campaign spend ÷ 250 leads = $20 CPL
Digital channels offer several advantages for lead cost tracking:
- Real-time cost monitoring and adjustment capabilities
- Granular audience targeting options
- Automated lead qualification processes
- Integration with CRM systems for complete funnel tracking
Traditional Marketing Cost Analysis
Traditional marketing requires a different approach to cost analysis, focusing on broader reach metrics and estimated conversion rates. The measurement process typically involves:
Traditional CPL Estimation:
(Total Campaign Cost + Distribution Costs) ÷ Estimated Lead Volume = Approximate CPL
Example: ($10,000 + $2,000) ÷ 400 estimated leads = $30 CPL
While traditional marketing channels maintain relevance for specific audience segments and brand-building initiatives, their cost structure presents unique challenges:
Is Your LinkedIn Not Delivering Results?
Just released: my new book to help professionals, entrepreneurs, and business owners maximize LinkedIn for real growth.
With years of LinkedIn expertise, Maximizing LinkedIn for Business Growth offers actionable steps to build your brand, expand your network, and drive results.
Start leveraging LinkedIn like never before—grab your copy now! Click the cover or button below to buy on Amazon.


Traditional marketing costs include multiple components that affect overall CPL and CPA calculations:
- Production costs (design, printing, video creation)
- Distribution expenses (media buying, placement fees)
- Geographic coverage considerations
- Long-term brand awareness value
The integration of social media analytics with traditional marketing metrics can help bridge the measurement gap and provide more accurate cost assessments. This hybrid approach enables better resource allocation and campaign optimization across all channels.
Understanding these cost structures leads naturally to examining the broader picture of return on ad spend (ROAS), which provides additional context for marketing investment decisions. The next section explores how to calculate and compare ROAS across different marketing channels.
2. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) Comparison
Return on Ad Spend provides crucial insights into marketing efficiency across channels. Digital advertising demonstrates particularly strong performance, with retargeting campaigns making customers 70% more likely to convert. This enhanced conversion potential significantly impacts overall ROAS calculations.
Digital ROAS Tracking Methods
Digital marketing platforms offer precise ROAS tracking through integrated analytics tools. The basic calculation framework remains consistent across channels:
Digital ROAS Formula:
Revenue Generated from Ads ÷ Total Ad Spend = ROAS Ratio
Example: $4,000 revenue ÷ $1,000 ad spend = 4:1 ROAS
Digital channels provide several advantages for ROAS measurement:
| Digital ROAS Feature | Benefit | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time tracking | Immediate performance insights | Automated analytics platforms |
| Campaign-level data | Granular performance analysis | Individual campaign tracking |
| Multi-channel attribution | Complete customer journey analysis | Cross-platform analytics |
| Audience segmentation | Targeted ROAS optimization | Demographic-based tracking |
Traditional Advertising Returns
Traditional marketing ROAS calculation requires a more comprehensive approach, incorporating both direct and indirect revenue impacts. The measurement process focuses on:
- Market penetration metrics
- Brand awareness increases
- Long-term customer value assessment
- Regional sales correlation analysis
While traditional channels may show lower immediate ROAS, their value often extends beyond direct revenue generation. Integration with digital marketing platforms can enhance tracking capabilities and provide more accurate ROAS measurements for traditional campaigns.
Key considerations for traditional ROAS assessment include understanding market reach, frequency of exposure, and brand recall rates helps create a more complete picture of traditional marketing effectiveness. These metrics, combined with sales data, enable more accurate ROAS calculations for traditional channels.
The relationship between ROAS and conversion rates provides essential context for marketing performance evaluation. The next section examines specific conversion rate metrics and their impact on overall marketing effectiveness.


3. Conversion Rate Metrics and Analysis
Conversion rates serve as critical indicators of marketing effectiveness across channels. Digital platforms demonstrate strong performance in driving direct purchases, with 58% of U.S. shoppers making purchases through social media. This direct correlation between engagement and conversion highlights the measurable impact of digital marketing efforts.
Digital Conversion Tracking
Digital marketing enables precise conversion tracking through sophisticated analytics platforms. The conversion measurement framework includes:
Digital Conversion Rate Formula:
(Number of Conversions ÷ Total Visitors) × 100 = Conversion Rate Percentage
Example: (50 conversions ÷ 1,000 visitors) × 100 = 5% conversion rate
Digital channels provide several distinct advantages for conversion tracking:
- Individual user journey mapping
- Multi-touch attribution modeling
- A/B testing capabilities
- Behavioral analysis tools
Traditional Marketing Conversion Measurement
Traditional marketing requires alternative approaches to measure conversion effectiveness. The process typically incorporates:
| Measurement Method | Application | Tracking Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Unique Codes/Coupons | Print Advertising | Redemption Tracking |
| Call Tracking | Broadcast Media | Dedicated Phone Lines |
| Foot Traffic Analysis | Outdoor Advertising | Store Visit Correlation |
| Survey Response | Brand Awareness | Customer Feedback |
Integration between traditional and digital tracking methods enhances overall conversion analysis. Implementing comprehensive KPI tracking across all channels provides deeper insights into marketing performance.
Key factors affecting conversion rates include:
- Channel-specific audience behavior patterns
- Message consistency across platforms
- Timing and frequency of exposure
- Call-to-action effectiveness
Understanding conversion patterns leads naturally to examining Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), as initial conversions often represent just the beginning of the customer relationship. The next section explores how to measure and compare CLV across different marketing channels.
4. Customer Lifetime Value in Different Marketing Channels
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) provides crucial insights into long-term marketing effectiveness. Research shows that a 1% increase in brand awareness leads to a 0.6% increase in long-term sales. This relationship between brand building and sustained revenue demonstrates the importance of measuring CLV across all marketing channels.
Digital CLV Calculation
Digital marketing platforms enable precise tracking of customer value through integrated ROI measurement tools. The comprehensive CLV framework includes:
Digital CLV Formula:
(Average Purchase Value × Purchase Frequency × Average Customer Lifespan) = Customer Lifetime Value
Example: ($100 × 4 annual purchases × 3 years) = $1,200 CLV
Digital channels offer several advantages for CLV measurement:
| CLV Component | Digital Tracking Method | Value Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase History | E-commerce Analytics | Transaction Value Tracking |
| Engagement Patterns | Behavioral Analytics | Interaction Frequency |
| Customer Retention | CRM Integration | Loyalty Metrics |
| Cross-channel Activity | Multi-touch Attribution | Unified Customer View |
Traditional Marketing CLV Assessment
Traditional marketing requires a more comprehensive approach to CLV measurement, incorporating both direct and indirect value indicators. Key considerations include:
- Brand loyalty development
- Referral value assessment
- Market presence impact
- Competitive positioning benefits
The integration of digital platforms with traditional marketing efforts enables more accurate CLV tracking across all channels. This hybrid approach provides deeper insights into customer value development and retention patterns.
Effective CLV optimization strategies include:
- Personalized communication programs
- Cross-channel engagement initiatives
- Customer segmentation refinement
- Loyalty program development
Understanding CLV patterns across channels provides essential context for Revenue per Visitor (RPV) analysis. The next section examines how to measure and optimize RPV across different marketing initiatives, building on the foundation of CLV insights.
5. Revenue per Visitor (RPV) Tracking
Revenue per Visitor serves as a crucial metric for evaluating marketing channel effectiveness. Digital channels demonstrate varying levels of trust and engagement, with native advertising showing 27% higher trust levels than social media ads (Source: PassiveSecrets). This trust differential significantly impacts visitor value across different marketing channels.
Digital RPV Measurement
Digital marketing enables precise tracking of visitor value through advanced performance analytics. The fundamental RPV calculation framework includes:
Digital RPV Formula:
Total Revenue Generated ÷ Total Number of Visitors = Revenue per Visitor
Example: $50,000 revenue ÷ 10,000 visitors = $5 RPV
Digital channels provide several distinct advantages for RPV optimization:
| RPV Component | Digital Advantage | Implementation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Traffic Quality | Precise targeting | Audience segmentation |
| Conversion Path | Journey tracking | Funnel analytics |
| User Behavior | Real-time monitoring | Behavioral analysis |
| Revenue Attribution | Direct tracking | E-commerce integration |


Traditional Marketing Revenue Attribution
Traditional marketing requires specialized approaches to measure visitor value. Implementation focuses on:
- Market segment analysis
- Geographic performance tracking
- Campaign timing correlation
- Brand impact assessment
Integration with digital analytics platforms enhances traditional marketing RPV measurement capabilities. This combined approach provides more accurate visitor value assessment across all channels.
Key factors influencing RPV include:
- Channel-specific engagement patterns
- Content relevance and quality
- Audience targeting precision
- Campaign timing optimization
Understanding RPV metrics leads naturally to examining attribution modeling and campaign tracking methods. The next section explores how to implement comprehensive attribution strategies across both traditional and digital marketing channels.
6. Attribution Modeling and Campaign Tracking
Attribution modeling reveals the true impact of each marketing touchpoint in the customer journey. Traditional channels maintain significant trust levels, with 82% of consumers trusting print ads and 80% trusting TV advertisements (Source: TheSocialShepherd). This trust factor must be integrated into comprehensive attribution models that span both traditional and digital channels.
Digital Attribution Models
Digital marketing enables sophisticated attribution tracking through advanced analytics platforms. Common attribution models include:
| Attribution Model | Best Use Case | Measurement Focus |
|---|---|---|
| First-Touch | Brand Discovery | Initial Contact Value |
| Last-Touch | Direct Response | Conversion Point |
| Linear | Equal Channel Credit | Full Journey Value |
| Position-Based | Key Touchpoint Focus | Critical Interactions |
Digital attribution provides several key advantages:
- Cross-device tracking capabilities
- Real-time data collection
- Multi-channel journey mapping
- Automated reporting systems
Traditional Marketing Attribution Challenges
Traditional marketing requires specialized attribution approaches that account for both direct and indirect impacts. Implementation focuses on:
Traditional Attribution Framework:
Market Penetration + Brand Lift + Sales Correlation = Attribution Value
Example: Measuring increased sales activity during specific campaign periods in targeted geographic areas
Integration with digital marketing platforms enhances traditional attribution capabilities through:
- Online-offline tracking integration
- Geographic performance analysis
- Brand awareness measurement
- Customer journey mapping
Effective attribution modeling requires consideration of several key factors:
Understanding the interplay between digital and traditional channels enables more accurate attribution modeling. This comprehensive approach to measurement provides deeper insights into marketing effectiveness and guides strategic resource allocation.
The combination of all these metrics – from CPL to attribution modeling – provides a complete framework for evaluating marketing ROI. The following FAQ section addresses common questions about implementing these measurements effectively.
Conclusion
Effective measurement of marketing ROI requires a comprehensive understanding of both traditional and digital metrics. By implementing the six key metrics discussed – from Cost per Lead to Attribution Modeling – businesses can make more informed decisions about their marketing investments.
Success in marketing measurement depends on:
- Consistent application of measurement frameworks
- Integration of traditional and digital metrics
- Regular analysis and optimization
- Adaptation to changing market conditions
For additional insights into optimizing your marketing performance, explore my guides on content marketing KPIs and digital marketing analytics.
Actionable advice for your digital / content / influencer / social media marketing.
Join 13,000+ smart professionals who subscribe to my regular updates.