The e-commerce world offers countless opportunities for businesses of all sizes. Two giants stand tall in this space: Amazon and Shopify. Each platform serves business owners in fundamentally different ways. Their distinct approaches to online selling can either accelerate your growth or limit your potential, depending on your specific needs.
As someone who has guided businesses through digital transformation since 2010, I’ve seen firsthand how choosing the right platform impacts long-term success. This choice shapes everything from your profit margins to your brand identity and customer relationships.
In this guide, you’ll discover the key differences between Amazon and Shopify. You’ll learn their strengths, limitations, and which business models thrive on each platform. This comparison will help you make an informed decision for your specific situation.
Understanding Amazon and Shopify: Platform Basics
Amazon and Shopify represent two distinct approaches to e-commerce. Amazon functions as a massive marketplace where you list products alongside millions of other sellers. Shopify operates as a platform that helps you build your own independent online store.
Amazon’s reach is massive. The platform has 98.07 million monthly active users in the U.S. alone. This built-in audience offers immediate exposure, but places you in a highly competitive environment.
Shopify takes a different approach. It provides the tools to create your own branded website where you control the entire shopping experience. This gives you independence but requires more effort to build traffic.
Let’s look at how these platforms compare across key features:
| Feature | Amazon | Shopify |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Marketplace | Website Builder/Platform |
| Audience | Built-in traffic | Build your own audience |
| Brand Control | Limited | Complete |
| Customer Relationship | Owned by Amazon | Owned by you |
| Getting Started | Quick | Requires setup |
This fundamental difference shapes everything from your day-to-day operations to your long-term growth potential. The right choice depends on your specific business goals and resources.
Business Model Comparison: Amazon vs Shopify
The business models of Amazon and Shopify differ dramatically. Understanding these differences helps you align your choice with your business strategy.
Amazon operates on a marketplace model. You pay Amazon for access to their customers. This model works like a digital shopping mall where Amazon owns the property and sets the rules. Shoppers come to Amazon, not specifically to your store.
Shopify uses a software-as-a-service model. You pay for the tools to build and run your own store. This works more like owning your own retail space, where you’re responsible for bringing in customers but have more freedom in how you operate.
Amazon’s Marketplace Approach
Amazon’s greatest strength is its massive customer base. The platform accounts for 39.6% of U.S. e-commerce sales as of 2025. This gives sellers immediate access to millions of ready-to-buy customers.
The tradeoff comes in control and margins. Amazon sets strict rules around how you present products, communicate with customers, and fulfill orders. They also take a significant cut of each sale through various fees.
For many businesses, this tradeoff makes sense. The access to Amazon’s audience outweighs the restrictions and fees.
Shopify’s Website Builder Approach
Shopify empowers you to create your own online store. You control the entire customer experience from discovery to post-purchase communication. This independence allows for stronger branding and deeper customer relationships.
The challenge with Shopify lies in traffic generation. Unlike Amazon, Shopify doesn’t provide customers. You need to use digital marketing for your e-commerce store to drive visitors to your site through strategies like SEO, social media, and paid advertising.
Let’s compare these approaches side by side:
| Aspect | Amazon Marketplace | Shopify Store |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Relationship | Amazon connects you with their customers | You find and nurture your own customers |
| Business Focus | Product optimization and competitive pricing | Brand building and marketing |
| Growth Model | Ranking higher in Amazon’s search results | Building website traffic through various channels |
| Value Proposition | Convenience and existing trust | Unique brand experience |
These business model differences create distinct operating environments that favor different types of products and strategies.
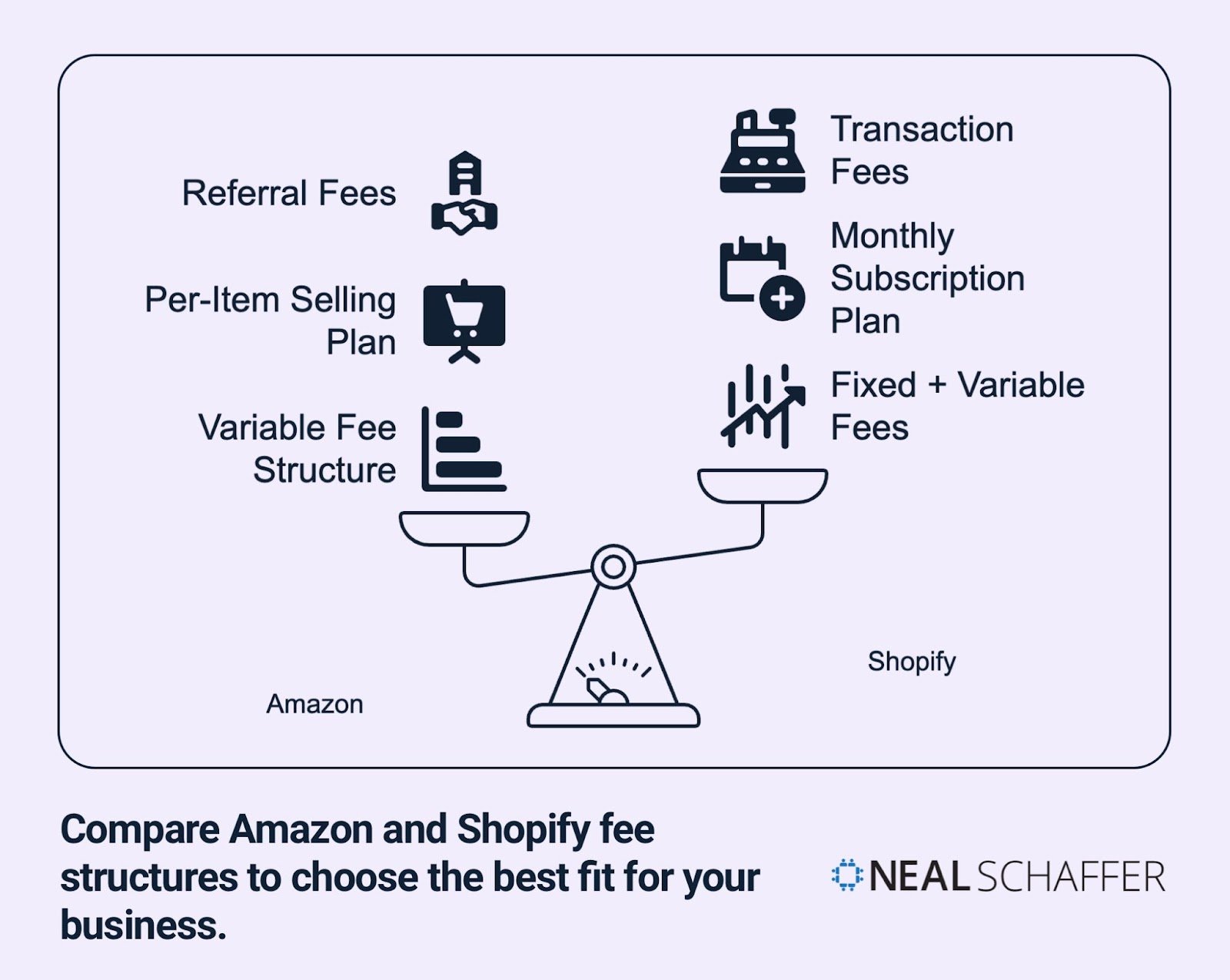
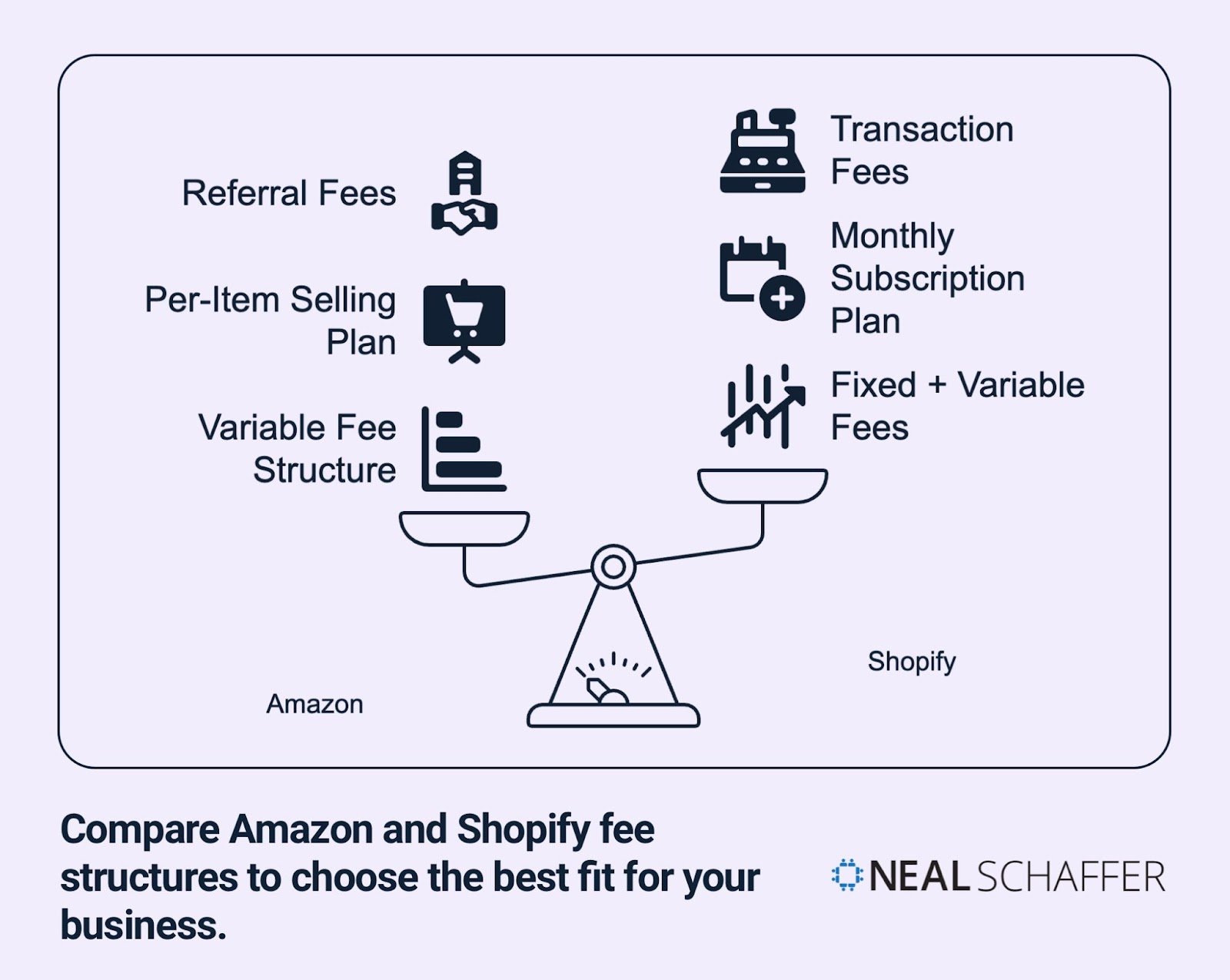
Fees and Pricing Structures
Cost plays a crucial role when choosing between Amazon and Shopify. Each platform uses a completely different pricing model that impacts your profit margins.
Amazon’s Fee Structure
Amazon uses a complex fee structure based primarily on categories and sales:
Is Your LinkedIn Working?
Just released: my new book to help professionals, entrepreneurs, and business owners maximize LinkedIn for real growth.
With years of LinkedIn expertise, Maximizing LinkedIn for Business Growth offers actionable steps to build your brand, expand your network, and drive results.
Start leveraging LinkedIn like never before—grab your copy now! Click the cover or button below to buy on Amazon.


- Selling plan fees: $0.99 per item (Individual plan) or $39.99 monthly (Professional plan)
- Referral fees: Category-dependent percentage of each sale (typically 8-15%)
- Fulfillment fees: Optional FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) costs based on item size/weight
- Additional fees: Storage, advertising, returns processing, etc.
Amazon’s fees directly impact your per-item profitability. For low-margin products, these fees can consume most or all of your potential profit.
The upside? You only pay significant fees when you make sales. This reduces upfront risk, especially for new businesses testing products.
Shopify’s Pricing Plans
Shopify uses a subscription model with three main tiers:
- Basic: Core e-commerce features for smaller businesses
- Shopify: Additional features for growing businesses
- Advanced: Comprehensive features for larger operations
Each plan includes hosting, security, and core e-commerce functionality. Shopify also charges transaction fees for each sale, though these are lower than Amazon’s referral fees.
The main difference? You pay Shopify monthly regardless of sales volume. This creates overhead that new businesses need to consider.
Here’s how the costs compare in practice:
| Cost Factor | Amazon | Shopify |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Fee | $0 (Individual) or $39.99 (Professional) | $29 (Basic) to $299 (Advanced) |
| Per-Sale Fees | 8-15% + $0.99 per item (Individual plan) | 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction |
| Additional Costs | FBA fees, advertising, storage | Apps, themes, domain, marketing |
| Cost Structure | Primarily variable (pay as you sell) | Fixed + variable |
These different fee structures create various break-even points depending on your sales volume and average order value.
The Hidden Costs to Consider
Beyond the obvious fees, both platforms involve additional costs that businesses often overlook:
For Amazon:
- Long-term storage fees can accumulate quickly
- Advertising is increasingly necessary to gain visibility
- Returns and customer service issues can generate extra costs
- Price competition often forces lower margins
For Shopify:
- Marketing costs to drive traffic
- App subscriptions for additional functionality
- Premium theme costs
- Development costs for customization
When analyzing costs, look beyond the basic fee structure to understand the total investment required for success on each platform.
Control and Customization
The level of control you have over your online presence differs dramatically between Amazon and Shopify. This factor often proves decisive for brand-focused businesses.
Amazon provides very limited customization. Your product listings follow Amazon’s strict template with minimal branding opportunities. The shopping experience, checkout process, and post-purchase communication all belong to Amazon. This standardization creates a consistent experience for shoppers but restricts your brand expression.
Shopify offers extensive control. You decide everything from your store’s design to the checkout experience. This freedom allows you to create a fully branded journey that builds customer loyalty and trust. For businesses focused on creating a distinctive brand identity, this represents a significant advantage.
Consider how successful brands use Shopify to express their unique identity and create memorable shopping experiences that customers return to repeatedly.
Brand Identity Considerations
Your brand identity faces different challenges on each platform:
On Amazon, your products compete primarily on price, reviews, and basic features. Your brand story, values, and unique selling propositions get minimal visibility. Shoppers often remember buying from “Amazon” rather than from your specific brand.
On Shopify, you create immersive brand experiences. You can tell your story, showcase your values, and build direct relationships with customers. This approach helps create loyal customers who connect with your brand beyond just product features and price.
This control extends to customer data as well. Amazon restricts access to customer information, limiting your ability to build direct relationships. Shopify gives you complete ownership of customer data, enabling personalized marketing and relationship building.
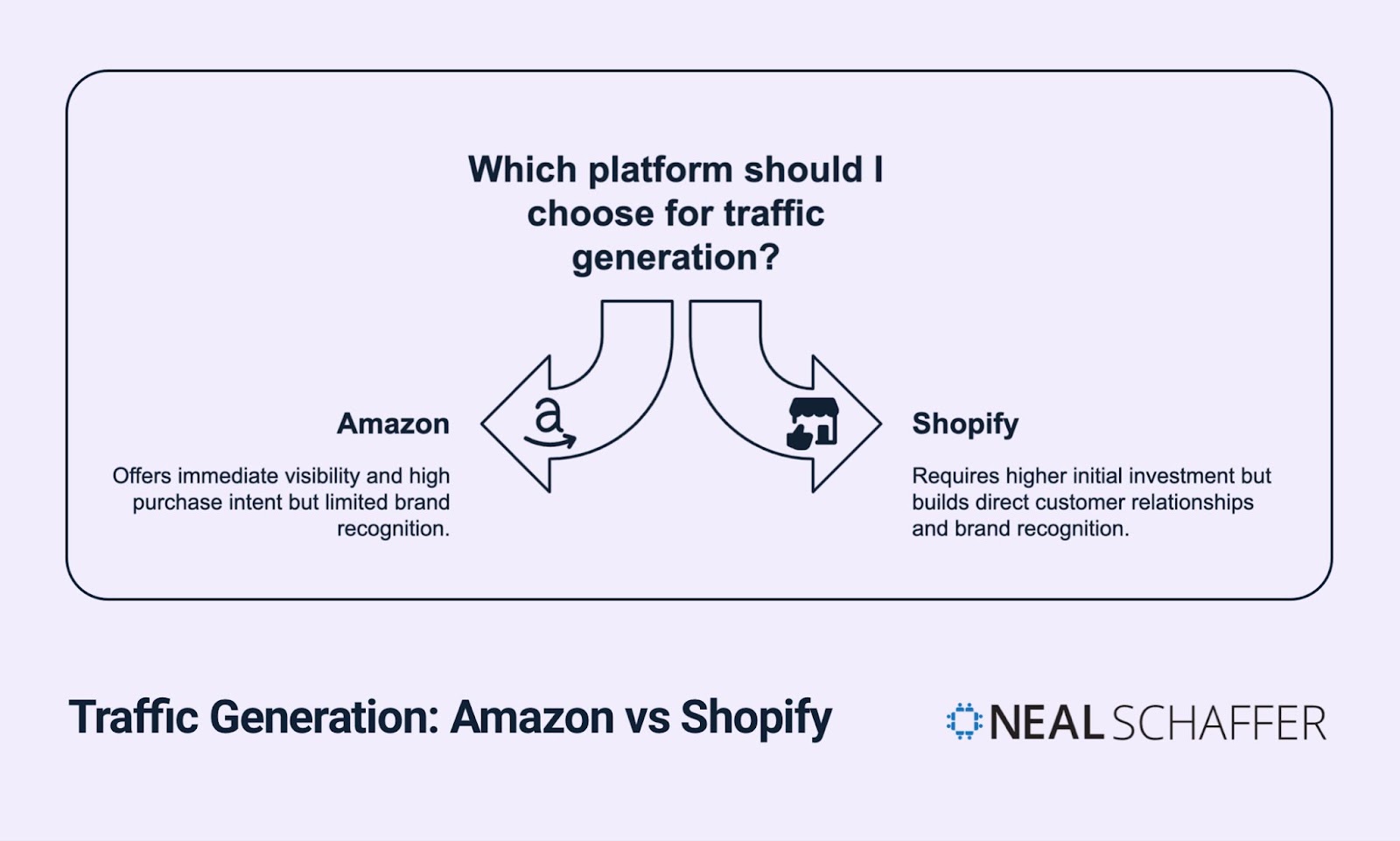
Traffic and Customer Acquisition
Getting your products in front of potential customers works very differently between these platforms. This difference significantly impacts your marketing strategy and budget.

Amazon’s Built-in Audience
Amazon’s greatest strength is its massive built-in audience. The platform attracted 3.25 billion global visitors in June 2024, with 53% coming from mobile devices. This traffic volume means products can start selling quickly without external marketing.
The platform functions as a search engine for products. About 90% of shoppers compare prices on Amazon before making a purchase elsewhere. This shopping behavior gives Amazon sellers instant access to high-intent buyers.
However, standing out among millions of products requires optimization. Success on Amazon depends on:
Shopify’s Marketing Requirements
Shopify stores start with zero traffic. Building an audience requires dedicated marketing efforts across multiple channels. This presents both a challenge and an opportunity.
The challenge lies in the need to invest time and money in traffic generation. You’ll need a comprehensive Shopify marketing strategy that might include:
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- Email marketing
- Paid advertising (Google, Facebook, Instagram, etc.)
The opportunity comes from building direct customer relationships and owning your traffic sources. Unlike Amazon, where customers belong to the platform, Shopify allows you to create lasting connections with visitors.
Let’s compare the traffic approaches side by side:
| Traffic Aspect | Amazon | Shopify |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Visibility | Immediate access to Amazon shoppers | Zero built-in traffic |
| Customer Intent | High purchase intent | Varies by traffic source |
| Marketing Investment | Primarily product listing optimization and Amazon ads | Comprehensive marketing across multiple channels |
| Competition | Direct competition with similar products | Competition for attention across the internet |
| Long-term Value | Limited brand recognition | Building owned audiences and channels |
The traffic model you prefer often depends on your marketing resources, expertise, and long-term business goals.
Fulfillment and Shipping Options
How you store, pack, and ship products impacts customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and profitability. Amazon and Shopify offer different approaches to order fulfillment.
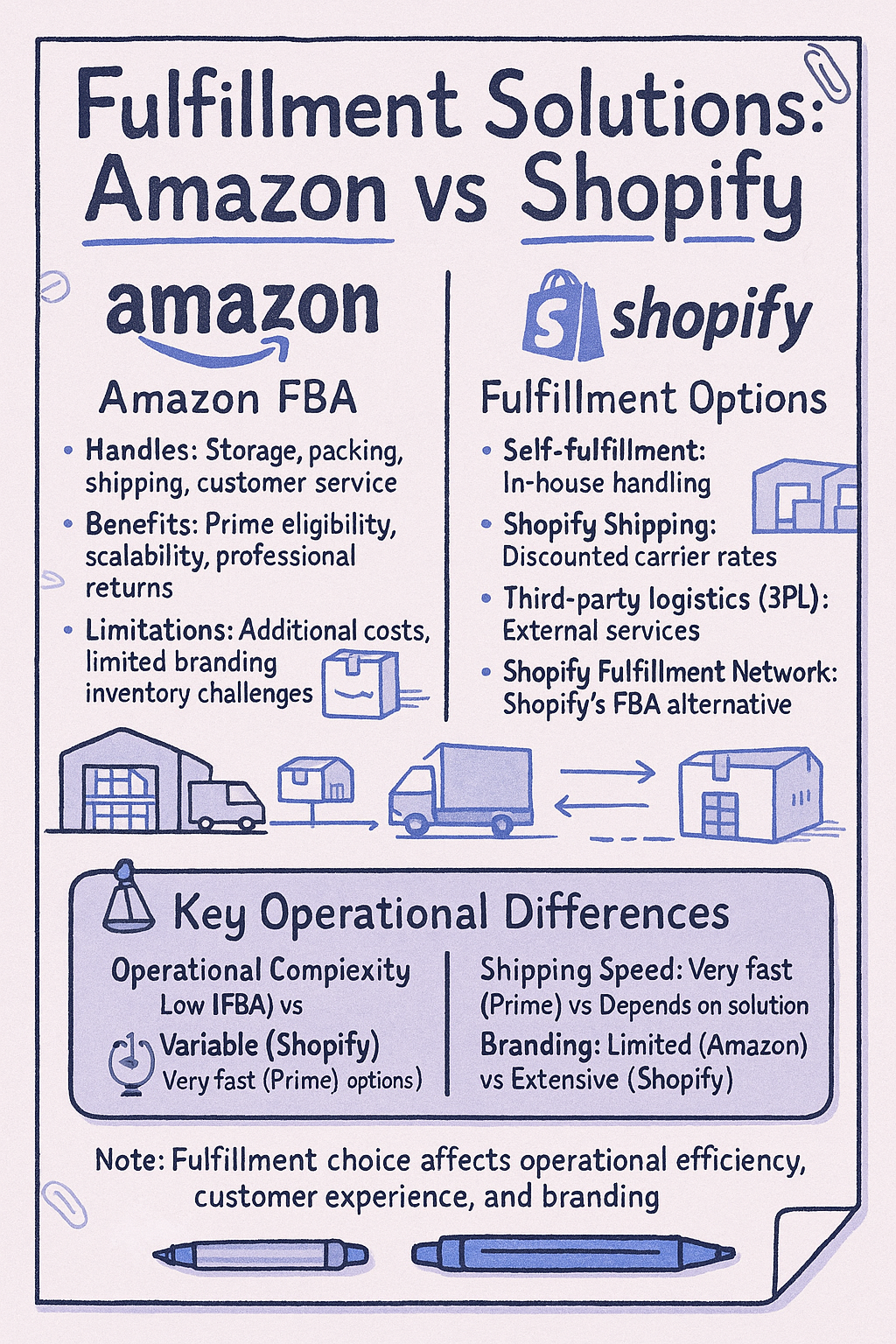

Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon)
Amazon’s FBA program handles storage, packing, shipping, and customer service for your products. This service leverages Amazon’s massive logistics network, including Prime shipping benefits. U.S. consumers spent $438.015 billion on Amazon in 2024, with Prime members representing a significant portion of these sales.
FBA offers several advantages:
- Prime eligibility increases sales potential
- Scalable fulfillment without infrastructure investment
- Professional handling of returns and customer service
- Multi-channel fulfillment options for some sellers
However, FBA comes with additional costs and inventory management challenges that impact profitability.
Shopify Shipping and Fulfillment
Shopify offers multiple fulfillment approaches:
- Self-fulfillment: Handling storage and shipping yourself
- Shopify Shipping: Discounted shipping rates with major carriers
- Third-party logistics (3PL): Integration with external fulfillment services
- Shopify Fulfillment Network: Shopify’s answer to FBA
This flexibility allows businesses to choose the fulfillment strategy that best fits their needs and growth stage. Small businesses often start with self-fulfillment, then graduate to 3PL services as they scale.
Shopify’s approach gives you more control over packaging, inserts, and the unboxing experience—important touchpoints for brand building.
Fulfillment Comparison
Here’s how the fulfillment options compare:
| Fulfillment Aspect | Amazon FBA | Shopify Options |
|---|---|---|
| Operational Complexity | Low (Amazon handles most aspects) | Varies (from high with self-fulfillment to low with 3PL) |
| Shipping Speed | Very fast (Prime 1-2 day shipping) | Depends on chosen solution |
| Cost Structure | Per-unit fees plus storage | Varies by solution |
| Branding Opportunities | Limited (Amazon-branded packaging) | Extensive (custom packaging options) |
| International Capabilities | Strong global network | Depends on chosen solution |
Your fulfillment choice affects not just operational efficiency but also customer experience and brand perception.
Which Platform Is Right for Different Business Types
Different business models thrive on different platforms. Understanding which environment aligns with your specific situation helps make the right choice.
Ideal Business Types for Amazon
Amazon typically works best for:
- New brands with limited marketing budgets – Leverage Amazon’s traffic without building your own audience
- Products with proven market demand – Compete effectively in established categories
- Commoditized products – Items where price and convenience drive purchase decisions
- Businesses with limited operations capacity – Use FBA to handle fulfillment
- Side hustles and part-time businesses – Amazon requires less operational oversight
Consider Amazon if immediate sales and minimal operational complexity are priorities over brand building.
Ideal Business Types for Shopify
Shopify typically works best for:
- Brand-focused businesses – Create distinctive shopping experiences
- Products with unique stories or features – Communicate value beyond price
- Subscription-based models – Build recurring revenue streams
- Businesses with marketing expertise – Effectively drive your own traffic
- Custom or made-to-order products – Manage complex product options
Choose Shopify if building a distinctive brand and owning customer relationships outweigh the need for immediate traffic.
The Hybrid Approach
Many successful businesses use both platforms strategically. This hybrid approach lets you:
1. Use Amazon as a customer acquisition channel and for additional revenue
2. Use Shopify as your brand hub and for higher-margin direct sales
3. Test new products on Amazon before adding them to your Shopify store
4. Drive Amazon customers to your Shopify store for repeat purchases
The key question isn’t always “which platform?” but “how can each platform serve different aspects of your business strategy?”
Decision Framework
Consider these questions when making your decision:
| If You Answer “Yes” To These Questions… | Consider This Platform |
|---|---|
| Do you need immediate sales without marketing investment? | Amazon |
| Is price the primary factor in purchase decisions for your product? | Amazon |
| Do you have limited time for operations management? | Amazon |
| Is building a distinctive brand important to your strategy? | Shopify |
| Do you want to own the customer relationship? | Shopify |
| Can you invest in marketing to drive your own traffic? | Shopify |
| Do you need high profit margins? | Shopify |
Your answers to these questions will guide you toward the platform that best aligns with your business goals and resources.


Conclusion: Making Your Final Decision
Choosing between Amazon and Shopify represents more than a platform decision—it’s a business model choice. The right answer depends on your specific goals, resources, and vision for your business.
Amazon offers access to millions of active buyers with minimal marketing effort. This comes at the cost of lower margins, limited brand control, and fierce competition.
Shopify provides complete ownership of your brand experience and customer relationships. This independence allows for higher margins and stronger customer loyalty but requires dedicated marketing effort to build traffic.
For many businesses, success comes from understanding how to leverage multiple channels in their digital strategy. Consider whether a hybrid approach might serve your business better than an either/or decision.
Start by evaluating your current capabilities:
- Marketing resources and expertise
- Operational capacity
- Product margins and pricing strategy
- Long-term brand vision
- Growth timeline expectations
Then map these capabilities to the platform that best supports your needs. Remember that your choice isn’t permanent—many businesses start on one platform and expand to the other as they grow.
Regardless of which platform you choose, the e-commerce opportunity continues to expand. With the right approach, both Amazon and Shopify can become powerful engines for business growth. The key lies in choosing the path that aligns with your unique business model and goals.
What matters most isn’t which platform you choose, but how effectively you execute your strategy within that environment.
Actionable advice for your digital / content / influencer / social media marketing.
Join 13,000+ smart professionals who subscribe to my regular updates.